Created
February 23, 2020 13:21
-
Star
(109)
You must be signed in to star a gist -
Fork
(35)
You must be signed in to fork a gist
-
-
Save krishnadey30/cb64bf875f29b5a6c91f79ea38a2ba4e to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.
Revisions
-
krishnadey30 created this gist
Feb 23, 2020 .There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters. Learn more about bidirectional Unicode charactersOriginal file line number Diff line number Diff line change @@ -0,0 +1,295 @@ # **C++ OOPS Concepts** The main aim of OOP is to bind together the data and the functions that operate on them so that no other part of the code can access this data except that function. ### **Characteristics of an Object Oriented Programming language**  #### Class It is a user-defined data type, which holds its own data members and member functions, which can be accessed and used by creating an instance of that class. A class is like a blueprint for an object. ```cpp class person { char name[50]; int id; public: void getDetails() {} } ``` The only difference between a structure and a class is that structure members have public access by default and class members have private access by default ##### Static Member functions in C++ A function is made static by using `static` keyword with function name. These functions work for the class as whole rather than for a particular object of a class. ```cpp class X { public: static void f() { // statement } }; int main() { X::f(); // calling member function directly with class name } ``` ##### Const Member functions in C++ When used with member function, such member functions can never modify the object or its related data members. ```clike // basic syntax of const Member Function void fun() const { // statement } ``` ------- #### Object An Object is an identifiable entity with some characteristics and behaviour. An Object is an instance of a Class. When a class is defined, no memory is allocated but when it is instantiated (i.e. an object is created) memory is allocated. ```cpp person p1; ``` Each object contains data and code to manipulate the data. Objects can interact without having to know details of each other’s data or code. ------- #### Encapsulation Encapsulation is defined as wrapping up of data and information under a single unit. In Object-Oriented Programming, Encapsulation is defined as binding together the data and the functions that manipulate them. Encapsulation also leads to *data abstraction or hiding*. ------ #### Abstraction Abstraction means displaying only essential information and hiding the details. Data abstraction refers to providing only essential information about the data to the outside world, hiding the background details or implementation. - *Abstraction using Classes* - *Abstraction in Header files* ------- #### Inheritance The capability of a class to derive properties and characteristics from another class is called Inheritance. - **Sub Class**: The class that inherits properties from another class is called Sub class or Derived Class. - **Super Class**: The class whose properties are inherited by sub class is called Base Class or Super class. - **Re-usability**: Inheritance supports the concept of “re-usability”, i.e. when we want to create a new class and there is already a class that includes some of the code that we want, we can derive our new class from the existing class. By doing this, we are reusing the fields and methods of the existing class. ##### Basic Syntax of Inheritance ```clike class Subclass_name : access_mode Superclass_name ``` ###### Public Inheritance This is the most used inheritance mode. In this the protected member of super class becomes protected members of sub class and public becomes public. ```clike class Subclass : public Superclass ``` ###### Private Inheritance In private mode, the protected and public members of super class become private members of derived class. ```clike class Subclass : Superclass // By default its private inheritance ``` ###### Protected Inheritance In protected mode, the public and protected members of Super class becomes protected members of Sub class. ```clike class subclass : protected Superclass ``` ##### Types of Inheritance in C++ In C++, we have 5 different types of Inheritance. Namely, 1. Single Inheritance: 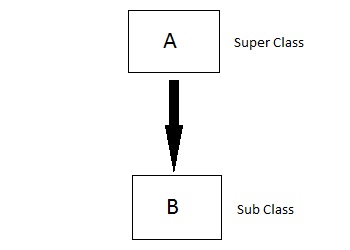 2. Multiple Inheritance: 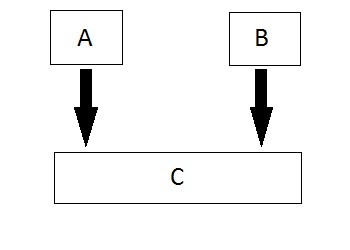 3. Hierarchical Inheritance: 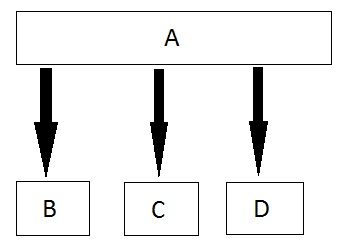 4. Multilevel Inheritance:  5. Hybrid Inheritance (also known as Virtual Inheritance):  ##### Points to Remember 1. Whether derived class's default constructor is called or parameterised is called, base class's default constructor is always called inside them. 2. To call base class's parameterised constructor inside derived class's parameterised constructor, we must mention it explicitly while declaring derived class's parameterised constructor. ```cpp class Base { int x; public: // parameterized constructor Base(int i) { x = i; cout << "Base Parameterized Constructor\n"; } }; class Derived : public Base { int y; public: // parameterized constructor Derived(int j):Base(j) { y = j; cout << "Derived Parameterized Constructor\n"; } }; ``` 3. All the Base class's constructors are called inside derived class's constructor, in the same order in which they are inherited. ```clike class A : public B, public C ; ``` ##### Ambiguity Resolution in Inheritance ```cpp class C : public A, public B { void view() { A :: display(); // Calling the display() function of class A. B :: display(); // Calling the display() function of class B. } }; //or int main() { B b; b.display(); // Calling the display() function of B class. b.B :: display(); // Calling the display() function defined in B class. } ``` #### Hybrid Inheritance and Virtual Class in C++ In Multiple Inheritance, the derived class inherits from more than one base class. Hence, in Multiple Inheritance there are a lot chances of ambiguity. ```clike class A { void show(); }; class B:public A { // class definition }; class C:public A { // class defintion }; class D:public B, public C { // class definition }; int main() { D obj; obj.show(); } ``` In this case both class B and C inherits function `show()` from class A. Hence class D has two inherited copies of function `show()`. In main() function when we call function `show()`, then ambiguity arises, because compiler doesn't know which `show()` function to call. Hence we use **Virtual** keyword while inheriting class. ```clike class B : virtual public A { // class definition }; class C : virtual public A { // class definition }; class D : public B, public C { // class definition }; ``` Now by adding virtual keyword, we tell compiler to call any one out of the two `show()` functions. Also see https://www.javatpoint.com/cpp-virtual-function ----- #### Polymorphism The word polymorphism means having many forms. **There are two types of polymorphism in C++:** 1. **Compile Time Polymorphism**: The overloaded functions are invoked by matching the type and number of arguments. This information is available at the compile time and, therefore, compiler selects the appropriate function at the compile time. It is achieved by function overloading and operator overloading which is also known as static binding or early binding. 2. **Run-time Polymorphism**: Run time polymorphism is achieved when the object's method is invoked at the run time instead of compile time. It is achieved by method overriding which is also known as dynamic binding or late binding 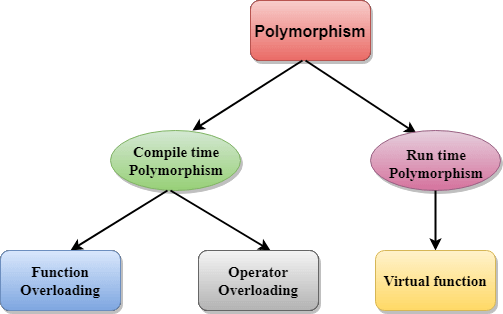 C++ supports operator overloading and function overloading. - *Operator Overloading*: The process of making an operator to exhibit different behaviours in different instances is known as operator overloading. - *Function Overloading*: Function overloading is using a single function name to perform different types of tasks. Polymorphism is extensively used in implementing inheritance. | Compile time polymorphism | Run time polymorphism | | :----------------------------------------------------------- | :----------------------------------------------------------- | | The function to be invoked is known at the compile time. | The function to be invoked is known at the run time. | | It is also known as overloading, early binding and static binding. | It is also known as overriding, Dynamic binding and late binding. | | Overloading is a compile time polymorphism where more than one method is having the same name but with the different number of parameters or the type of the parameters. | Overriding is a run time polymorphism where more than one method is having the same name, number of parameters and the type of the parameters. | | It is achieved by function overloading and operator overloading. | It is achieved by virtual functions and pointers. | | It provides fast execution as it is known at the compile time. | It provides slow execution as it is known at the run time. | | It is less flexible as mainly all the things execute at the compile time. | It is more flexible as all the things execute at the run time. |