Your task is implement a better malloc logic in malloc.c to improve the speed and memory usage.
# build
| package main | |
| import "fmt" | |
| import "github.com/skelterjohn/go.matrix" | |
| func main() { | |
| dmat := matrix.Zeros(4, 3) | |
| dmat.Set(0, 1, 7) | |
| fmt.Println(dmat) |
Your task is implement a better malloc logic in malloc.c to improve the speed and memory usage.
# build
| /* exported stringifyJSON */ | |
| const stringifyJSON = (obj) => { | |
| /* ------ Define submodules ------- */ | |
| let result = "" | |
| const stringifyString = (elem) => { | |
| // `elem` : Element of the input object. It's data type is string. | |
| result += `"${elem}"`; | |
| return result; |
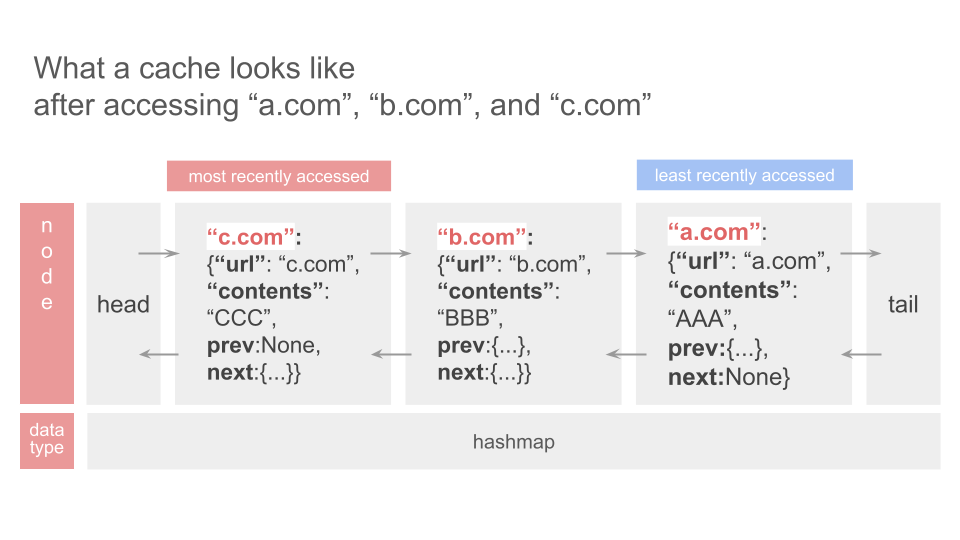
cache.py records a cache that stores the most recently accessed N pages where N is a given number. It, in addition, returns the cache starting with the most recently accessed page and ending with the least recently accessed one. The time complexity of updating a cache is mostly done in O(1) time. This is because a doubly linked list, which requires only O(1) time to add or delete element when we know the index of it, stores a cache. The nodes of the doubly linked list are hashmap type. A node has an url as a key and other information (the page url, contents, previous node, next node) as a value.
This is a big picture that illustrates what a cache looks like after accessing “a.com”, “b.com”, and “c.com”.
This program finds one or multiple word(s) that can be consisted of the characters of the word you input. It eventually returns a word that has the highest score among them.
e.g., it should find ["at", "cat"] if you input "tac" and finally returns "cat".
| # How to run | |
| # python3 findAnagram1.py | |
| # ----- define functions ----- # | |
| import re | |
| def sortWordsInDictionary(original_dictionary): # The time complexity is NlogN where N is the number of words in a dictionary | |
| # returns a hashmap whose keys are an alphabetically sorted words and values are original words ex) {"aet" : "eat", "tea"} | |
| dictionary = {} |