- login to 'AWS Management Console' (https://aws.amazon.com/console/)
- from 'Services'(in navbar) choose 'EC2'
- from 'Create Instance' section, click on 'Launch Instance'
- then select 'AMI' (Amazon Machine Image), we will be using 'Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS (HVM)' as example
- select 'Instance Type' as per your requirement
- then click 'Next:Configure Instance Details' to continue
change 'Configure Instance Details' or used as default settings
Install jq in ubuntu:
sudo apt install jq
diff <(jq -S . file1.json) <(jq -S . file2.json)
| require 'csv' | |
| def self.fetch_object_sizes | |
| CSV.open(Rails.root.to_s + '/tables.csv', 'wb') do |csv| | |
| csv << ['Table Name', 'Bytes Per Object'] | |
| ApplicationRecord.connection.tables.collect do |table_name| | |
| table_name.upcase! | |
| segment_names = [table_name] | |
| count = ApplicationRecord.connection.exec_query("select count(*) from #{table_name}").rows.flatten.first.to_f |
| ### Latest Blog | |
| http://developers.dymo.com/2018/05/29/updated-js-sdk-and-dls/ | |
| ### System Requirement for DYMO v8.7.3, works with JS SDK 3.0 | |
| ``` | |
| Windows 7 SP1 or later (32-bit or 64-bit) | |
| Windows 8 (32-bit or 64-bit) | |
| Windows 8.1 (32-bit or 64-bit) |
Ubuntu
Info about RAM slots and max support: https://askubuntu.com/questions/673408/command-to-check-ram-slots-in-motherboard
Git
Get the list of contributors for repository:
git log --format='%aN' | sort -u
| ENV["RAILS_ENV"] ||= 'test' | |
| require File.expand_path("../../config/environment", __FILE__) | |
| require 'rspec/rails' | |
| require 'rspec/autorun' | |
| require 'capybara/rspec' | |
| require 'webmock/rspec' | |
| require 'factory_girl' | |
| require 'factory_girl_rails' | |
| Dir[Rails.root.join("spec/support/**/*.rb")].each {|f| require f} |
| var SR = SR || {}; | |
| $(function() { | |
| $(document).on("click", "a[data-remote-popup]", function(event) { | |
| event.preventDefault(); | |
| SR.Modal.showRemoteModal(this.href, this.dataset.title, this.dataset.modal_class); | |
| }); | |
| $(document).on("click", "a[data-window]", function(event) { | |
| event.preventDefault(); |
post has_many :comments
comment belongs_to author
class CommentsController < ApplicationController
def users_comments
posts = Post.all
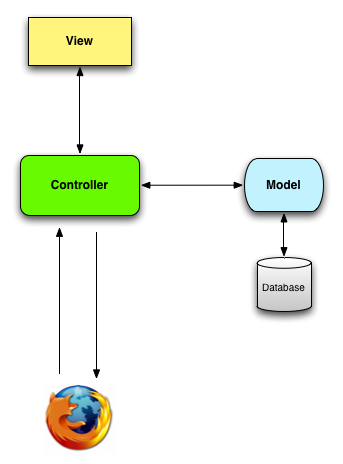
comments = posts.map(&:comments).flatten###MVC Model–view–controller (MVC) is a software architectural pattern mostly for implementing user interfaces (but not only for user interface). It divides a given software application into three interconnected parts, so as to separate internal representations of information from the ways that information is presented to or accepted from the user.
When interacting with a Rails application, a browser sends a request, which is received by a web server and passed on to a Rails controller, which is in charge of what to do next. In some cases, the controller will immediately render a view, which is a template that gets converted to HTML and sent back to the browser. More commonly for dynamic sites, the controller interacts with a model, which is a Ruby object that represents an element of the site (such as a user) and is in charge of communicating with the database. After invoking the model, the c